Carotenoids for skin health
Carotenoids are a family of phytonutrients that include beta-carotene, lutein and lycopene.
Astaxanthin and zeaxathin are also members of this family.
Beta-carotene
Beta-carotene is a fat-soluble antioxidant and precursor to vitamin A and is therefore called provitamin A.
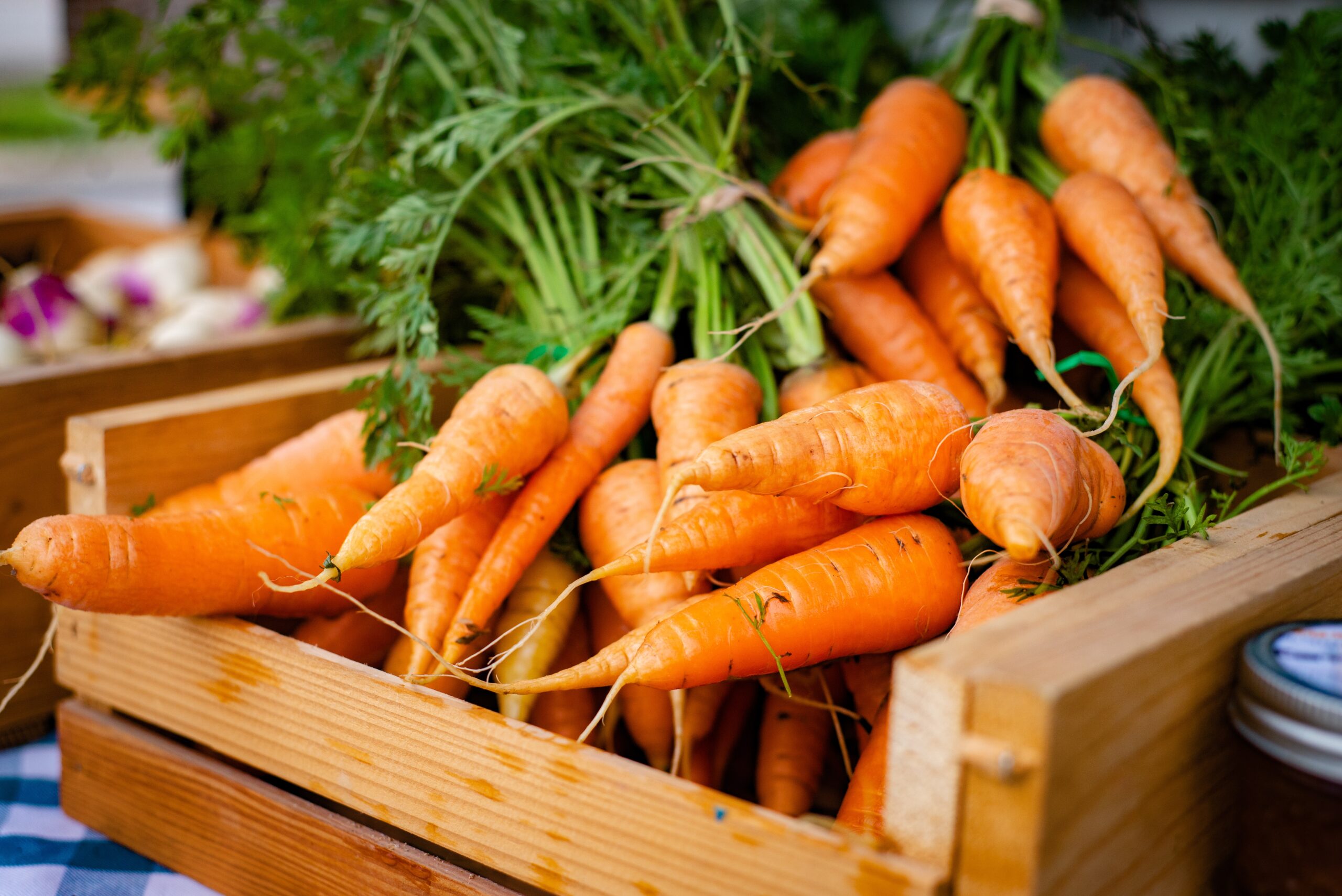
It is found in yellow and orange foods such as carrots, sweet potato, papaya, pumpkins and yellow and orange peppers but also in green leafy vegetables such as spinach and arugula (rocket salad).
Caution! Supplementation of large amounts of beta-carotene should be avoided since some studies indicate an increased risk of cancer.
Lutein
Lutein is known to protect the eyes from harmful UV radiation.
It is found in eggs, kale, spinach, broccoli and other green vegetables.
Lycopene
Lycopene is a fat-soluble antioxidant that is known to protect the skin from photooxidative stress.
It is found in tomatoes, mainly in the peel, watermelon, blood orange and blood grape.

Carotenoids and the skin
Several studies show that carotenoids protect the skin, here are a few examples:
- Lycopene and beta-carotene in combination with vitamin E and vitamin C reduce the formation of MMP enzymes.
- One study showed that beta-carotene in combination with vitamin E protect the skin against erythema (redness of the skin) caused by UV-radiation.
- Beta-carotene and lycopene can increase blood flow and regulate skin structure and hydration. Intake of lycopene and beta-carotene should always be combined with vitamin E to protect them from being oxidized.
- People with a high intake of green and yellow vegetables had fewer wrinkles.
- One study showed that 40g tomato puree, containing 16 mg lycopene, for ten weeks reduced the redness caused by UV radiation by 40 percent.
Nutrition Matters Skin –
Your complete guide to beautiful skin from within!
References
Offord E.A et.al. Photoprotective potential of lycopene, beta-carotene, vitamin E, vitamin C and carnosic acid in UVA-irradiated human skin fibroblasts. Free radical biology and medicine. 2002; 32(12): 1293-1303
Stahl, W.; Heinrich, U.; Jungmann, H.; Sies, H.; Tronnier, H. Carotenoids and carotenoids plus vitamin E protect against ultraviolet light-induced erythema in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71:795-798
Stahl W, Heinrich U, Wiseman S, Eichler O, Sies H, Tronnier H. Dietary tomato paste protects against ultraviolet light–induced erythema in humans. J. Nutr. 2001;131:1449-1451
Cosgrove M.C, Franco O.H, Granger S.P, Murray P.G, Mayes A.E. Dietary nutrient intakes and skin-aging appearance among middle aged American women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:1225-31