What are anthocyanins and why are they important for skin health?
Anthocyanidins are found in dark purple, blue, black and red plants, especially in berries such as blueberries, black currants, blackberries and raspberries. It is the anthocyanidins that give the berries their blue, purple and black color.
The anthocyanidins belong to the family of phytonutrients called flavonoids. They have been used as active ingredients in traditional medicine and are known for their antioxidant properties and help reduce damage to cells caused by free radicals. They also have anti-inflammatory properties and affect collagen metabolism.
MMP-enzymes are activated when the skin is exposed to the sun’s UV radiation. One of the most important effect that anthocyanidins have on the skin is that they reduce the breakdown of collagen by blocking MMP-enzymes that break down collagen. This means that by eating foods that contain anthocyanidins you can increase the protection of the skin from damage caused by UV-radiation from the sun.
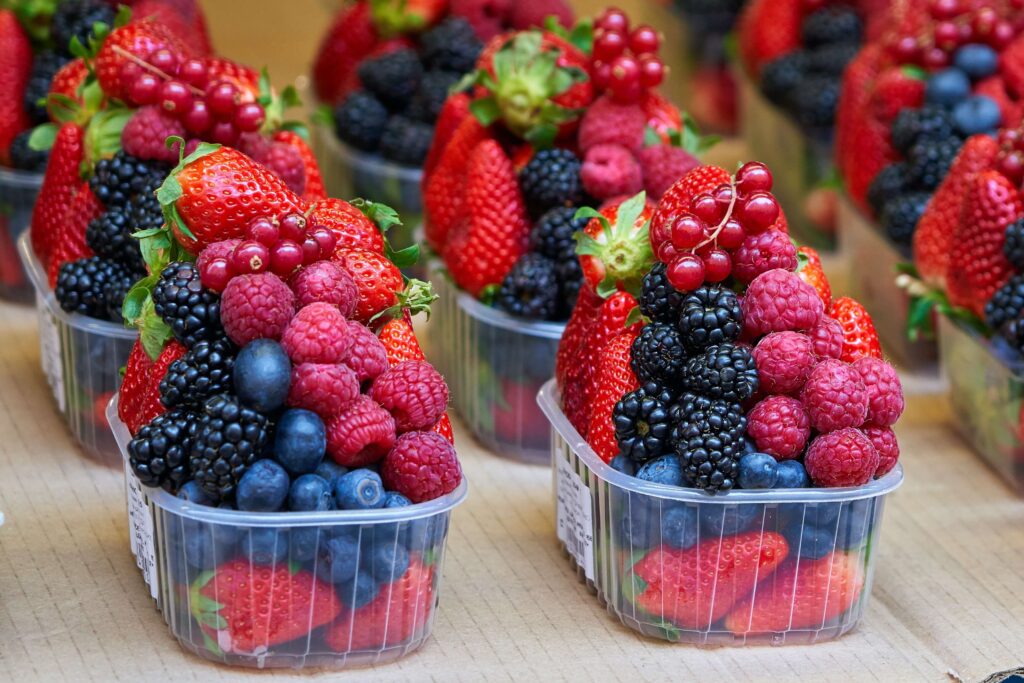

How can anthocyanidins reduce signs of skin aging?
One study examined the ability of anthocyanidins to reduce swelling in a group of women and showed good results. The researchers explain that the ability of anthocyanidins to strengthen collagen, makes blood vessels less likely to leak fluid from the blood vessels into tissues, which reduced swelling.
The participants in the study also reported that their skin improved, which resulted in that a follow-up study was performed. The results of the follow-up study (which, however, were not published), showed that intake of a supplement containing extracts from blueberries and grapes (anthocyanidins) reduced skin aging.
The scientists measured some parameters of skin aging and noticed reduced depth of wrinkles and better elasticity in the skin, which is likely to be due to skin’s collagen being strengthened. They also saw that the skin had a SPF equivalent to 15, and reduced appearance of so called spider veins, after 12 weeks.
Anthocyanidins reduce damage from UV-radiation
Bog blueberry, also called Odon, is a berry that is easily confused with blueberries as they look very similar and grow in similar environments. Studies on the effect of bog blueberry on human fibroblast cells show that it protects against the breakdown of collagen by inhibiting MMP enzymes.
Exposure to UVB radiation increases the levels of inflammatory substances, as previously described. Bog blueberry extract reduced the levels of these inflammatory substances.
Not just the skin
The effect of MMP-enzymes affects not only the appearance of the skin but also the spread of cancer, metastasis. One study of prostate cancer cells found that extracts from blueberries, containing anthocyanidins and proanthocyanidins, a form of anthocyanidin, inhibited MMP-2 and MMP-9. In this study, the researchers concluded that it protects against metastasis (the spread of cancer) because it reduces the tumors’ ability to break down healthy connective tissue around them, which is important for its ability to spread.
Blueberry extracts were shown in one study to reduce pain and inflammation in people with osteoarthritis, the most common joint disease worldwide. Although the researchers did not consider it to be significant, a certain reduction in certain MMP enzymes was seen in the participants in the group who received blueberry extract.
Nutrition Matters Skin –
Your complete guide to beautiful skin from within!
Reference
Nichols J.A, Katiyar S.K. Skin photoprotection by natural polyphenols: anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and DNA repair mechanisms. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010;302